THANK YOU FOR SUBSCRIBING
Editor's Pick (1 - 4 of 8)

Disruptive changes & Digitalization in the Energy sector
Anand Menon, CTO - Eng Tech Energy Management ASEAN, Siemens


Anand Menon, CTO - Eng Tech Energy Management ASEAN, Siemens
Digital twins and simulation software are helping design better and more resilient electric power grids
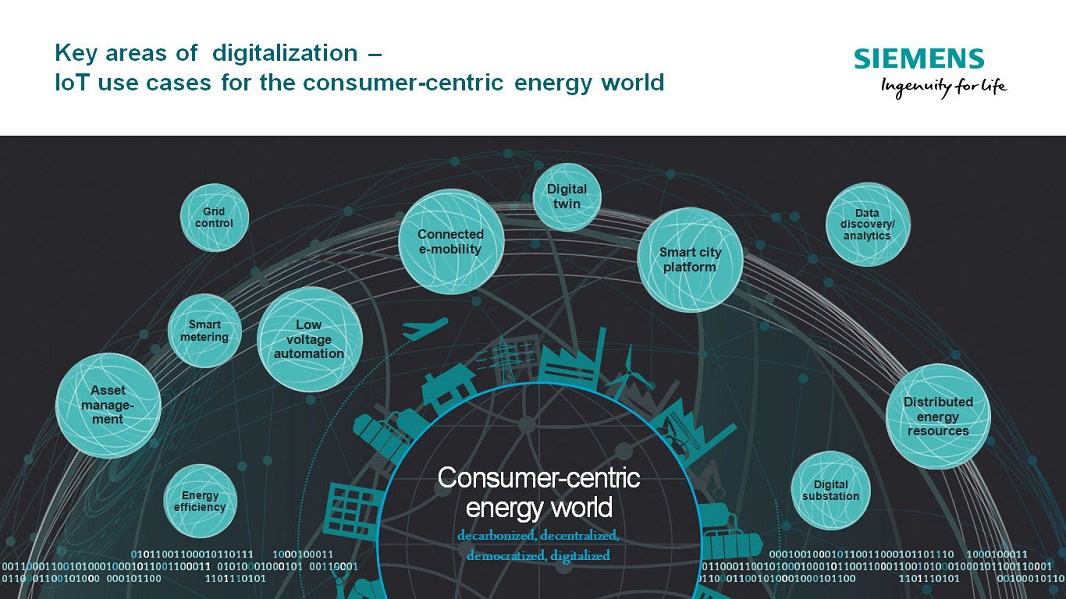
 The Siemens integrated platform strategy combining the grid control (OT) platform and the grid applications (IT) platform offers added value to utilities through various use cases. Using smart meter information in OT platform helps grid operators to identify network problems before receiving customer calls. That enables faster outage detection and restoration time. On the other hand, the IT platform utilizes outage information from the OT platform to notify the consumers pro-actively about the outage situation, restoration activities, expected duration via e.g. web-channel or mobile app.
Furthermore, the IT platform also offers an analytics environment based on state of the art technology, and advanced analytics applications to leverage more value from the existing data.
In order to enable cross vertical use cases, new business models, and new service offerings to consumers and prosumers in a networked ecosystem with multiple infrastructure domains, Siemens has launched a cloud-based, open protocol operating system for Internet of Things termed MindSphere.
Another technology with disruptive potential is Blockchain which can be used for a variety of applications, ranging from recording transactions between business partners to peer-to-peer ( P2P) energy trading in and between distribution grids ( cells) thus leading the transformation to a robust non-hierarchical energy system.
Nature of new businesses
With the increase in renewable sources in the energy mix and advent of Smart Grid, there has been substantial impact in businesses serving the electricity value chain from generation to consumption.
At a generation level, there are a host of renewable energy technologies such as wind, solar PV, solar concentrated, biomass, biogas, geo-thermal with their interfaces to the grid such as power electronics.
There also is a great demand for high efficiency fossil-fired plants such as combined cycle natural gas, apart from equipment to reduce CO2 emissions such as flue gas filtration.
In transmission, HVDC and FACTS play a major role along with grid strengthening equipment such as series and shunt capacitor banks, phase shifting transformers and reactors. Off-shore platforms with switchgear and transformers also play a role in connecting the renewable production to the mainland.
In distribution, the impact is seen in the requirement of advanced distribution management systems, substation automation and feeder automation systems. To accommodate renewables, storage systems are increasingly in demand. Automated Metering Infrastructures (AMI) are being rapidly deployed along with associated communication technologies to increase transparency in the grid which also serves as the foundation for applications such as Time of Use Tariff rates, Pre-payment schemes, theft detection, remote connect/disconnect, and Demand response applications.
Utilities are embarking on OT/ IT integration and data analytics to leverage upon the large amounts of data collected and to have a single integrated platform addressing multiple applications.
In consumption, energy efficiency has emerged as a priority to optimize energy usage especially in markets where energy government subsidies are gradually getting lifted and the electricity price passed on to the consumer. This has resulted in focus on buildings that consume upwards of 40 percent energy. Green and smart buildings need a robust building management system along with surveillance and fire security. Higher efficiency variable speed electric drives and chillers besides lighting appliances are sought to improve efficiency and reduce consumption. Residential consumer awareness is enhanced through Web Portals or In-home displays.
Words of caution.
With Information and Communication technologies penetrating down to the distribution networks, growing interconnections create more points for potential cyber attacks to critical infrastructure such as substations, micro grids, energy management systems, etc. It is highly recommended to implement cyber security controls from a holistic perspective encompassing people, processes and products (3 P) principles.
Check This Out: Top Energy Management Solution Companies
The Siemens integrated platform strategy combining the grid control (OT) platform and the grid applications (IT) platform offers added value to utilities through various use cases. Using smart meter information in OT platform helps grid operators to identify network problems before receiving customer calls. That enables faster outage detection and restoration time. On the other hand, the IT platform utilizes outage information from the OT platform to notify the consumers pro-actively about the outage situation, restoration activities, expected duration via e.g. web-channel or mobile app.
Furthermore, the IT platform also offers an analytics environment based on state of the art technology, and advanced analytics applications to leverage more value from the existing data.
In order to enable cross vertical use cases, new business models, and new service offerings to consumers and prosumers in a networked ecosystem with multiple infrastructure domains, Siemens has launched a cloud-based, open protocol operating system for Internet of Things termed MindSphere.
Another technology with disruptive potential is Blockchain which can be used for a variety of applications, ranging from recording transactions between business partners to peer-to-peer ( P2P) energy trading in and between distribution grids ( cells) thus leading the transformation to a robust non-hierarchical energy system.
Nature of new businesses
With the increase in renewable sources in the energy mix and advent of Smart Grid, there has been substantial impact in businesses serving the electricity value chain from generation to consumption.
At a generation level, there are a host of renewable energy technologies such as wind, solar PV, solar concentrated, biomass, biogas, geo-thermal with their interfaces to the grid such as power electronics.
There also is a great demand for high efficiency fossil-fired plants such as combined cycle natural gas, apart from equipment to reduce CO2 emissions such as flue gas filtration.
In transmission, HVDC and FACTS play a major role along with grid strengthening equipment such as series and shunt capacitor banks, phase shifting transformers and reactors. Off-shore platforms with switchgear and transformers also play a role in connecting the renewable production to the mainland.
In distribution, the impact is seen in the requirement of advanced distribution management systems, substation automation and feeder automation systems. To accommodate renewables, storage systems are increasingly in demand. Automated Metering Infrastructures (AMI) are being rapidly deployed along with associated communication technologies to increase transparency in the grid which also serves as the foundation for applications such as Time of Use Tariff rates, Pre-payment schemes, theft detection, remote connect/disconnect, and Demand response applications.
Utilities are embarking on OT/ IT integration and data analytics to leverage upon the large amounts of data collected and to have a single integrated platform addressing multiple applications.
In consumption, energy efficiency has emerged as a priority to optimize energy usage especially in markets where energy government subsidies are gradually getting lifted and the electricity price passed on to the consumer. This has resulted in focus on buildings that consume upwards of 40 percent energy. Green and smart buildings need a robust building management system along with surveillance and fire security. Higher efficiency variable speed electric drives and chillers besides lighting appliances are sought to improve efficiency and reduce consumption. Residential consumer awareness is enhanced through Web Portals or In-home displays.
Words of caution.
With Information and Communication technologies penetrating down to the distribution networks, growing interconnections create more points for potential cyber attacks to critical infrastructure such as substations, micro grids, energy management systems, etc. It is highly recommended to implement cyber security controls from a holistic perspective encompassing people, processes and products (3 P) principles.
Check This Out: Top Energy Management Solution Companies
Weekly Brief
I agree We use cookies on this website to enhance your user experience. By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies. More info
Read Also